Introduction
Producing is an industry driven by accuracy and proficiency, and molds assume a pivotal part in this cycle. Two of the most regularly utilized molds are die casting mold and plastic mold. In spite of the fact that they fill comparative needs, the materials, techniques, and applications engaged with these two cycles are unfathomably unique. Understanding these qualifications can help producers, creators, and specialists go with informed choices while choosing the proper assembling technique for their items.
Die Casting Mold Manufacturing
-
Overview of Die Casting
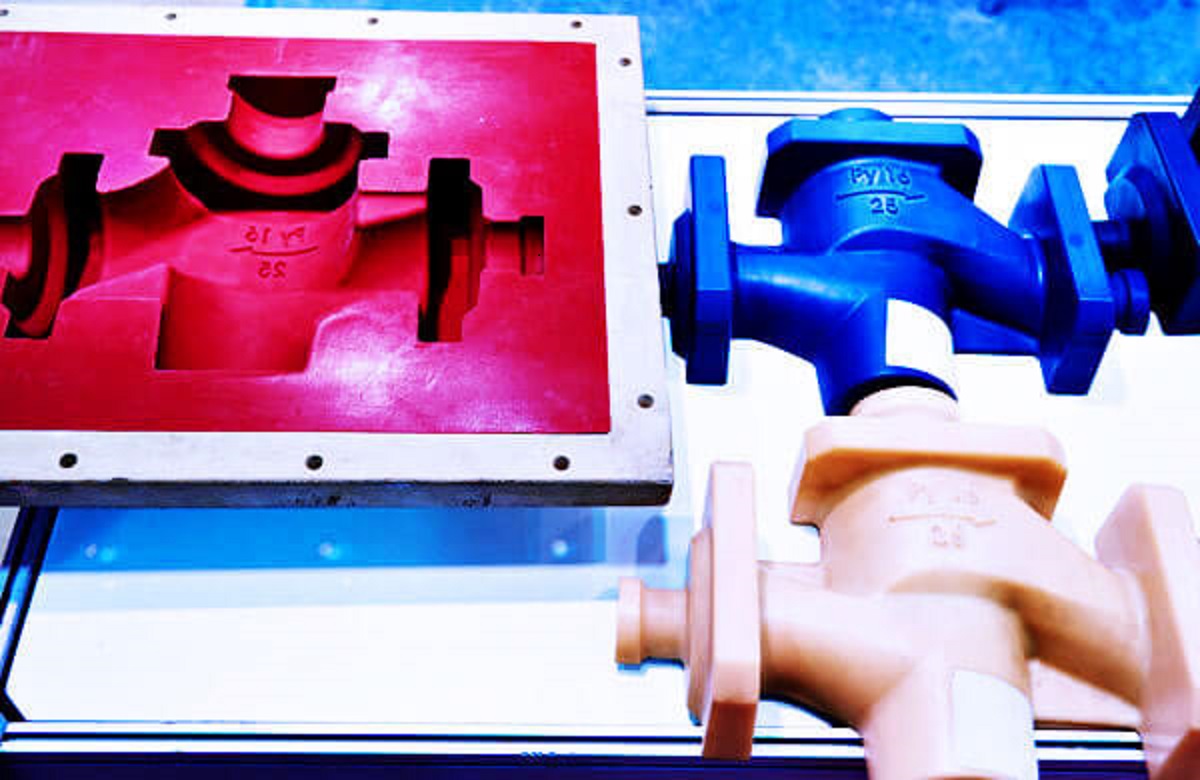
Pass on projecting is a metal projecting cycle wherein liquid metal is infused under high tension into a shape pit. The cavity is framed by two solidified steel passes on that have been machined into the ideal shape. After the metal hardens, the form is opened, and the completed part is catapulted. This cycle is broadly utilized in ventures like car, aviation, and gadgets to deliver metal parts with complex plans and high accuracy.
-
Materials Used in Die Casting
Normal metals utilized in kick the bucket projecting incorporate aluminum, magnesium, zinc, and copper. Every metal offers special properties:
- Aluminum: Known for being lightweight and consumption safe, ideal for auto parts.
- Magnesium: The lightest primary metal, offering a decent solidarity to-weight proportion.
- Zinc: Effectively castable and solid, frequently utilized for perplexing plans.
- Copper: Offers phenomenal conductivity, making it reasonable for electrical parts.
-
Die Casting Mold Design
Die casting molds, or on the other hand bites the dust, are regularly produced using solidified steel to get through the high tensions and temperatures engaged with the cycle. The plan of the pass on should consider factors like shrinkage, stream of the liquid metal, and cooling times to guarantee the end result meets the ideal details.
-
The Die Casting Process
The die casting process involves several stages:
- Bracing: The shape parts are cinched together safely.
- Infusion: Liquid metal is infused into the shape under high tension.
- Cooling: The metal is permitted to cool and harden inside the shape.
- Launch: The shape is opened, and the set part is catapulted.
- Managing: Abundance material is taken out from the completed part.
-
Advantages and Limitations of Die Casting
Benefits:
- High Accuracy: Produces leaves behind close resistances and complex shapes.
- Toughness: Metal parts areas of strength for are, safe, and erosion safe.
- Effectiveness: Ideal for high-volume creation runs.
Impediments:
- High Beginning Expenses: The tooling for pass on projecting molds is costly, making it less appropriate for little creation runs.
- Material Limitations: Bite the dust projecting is restricted to explicit metals, and not all are appropriate for this interaction.
Plastic Mold Manufacturing
1. Overview of Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic infusion shaping is a cycle where liquid plastic is infused into a form hole, which is then cooled and set to frame a plastic part. The form is normally made of steel or aluminum and comprises of two parts that meet up to make the ideal shape. This technique is broadly utilized for delivering plastic parts in businesses like customer merchandise, hardware, and medical care.
2. Materials Utilized in Plastic Embellishment
Countless thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics can be used in implantation shaping, including:
Polyethylene (PE): Routinely used for packaging and holders.
Polypropylene (PP): Offers substance impediment and toughness, oftentimes used in vehicle parts.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): A strong plastic used for equipment and vehicle parts.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): Used being developed materials and plumbing.
3. Plastic Form Plan
Plastic mold are intended to oblige the progression of liquid plastic and guarantee appropriate cooling to keep away from deformities, for example, distorting or air pockets. The plan should likewise consider the shrinkage of the plastic as it cools and cements.
4. The Plastic Infusion Trim Interaction
The plastic infusion forming process includes a few stages:
Cinching: The shape parts are braced together.
Infusion: Liquid plastic is infused into the shape pit.
Cooling: The plastic cools and hardens inside the shape.
Launch: The shape is opened, and the part is shot out.
Wrapping up: Any overabundance material is taken out, and the part is done as the need might arise.
5. Benefits and Limits of Plastic Infusion Trim
Benefits:
Flexibility: Equipped for delivering leaves behind different shapes and sizes.
Savvy for Huge Runs: While the underlying tooling cost is high, the per-part cost diminishes essentially with enormous creation volumes.
Material Adaptability: A wide assortment of plastics can be utilized, taking into consideration customization in light of explicit requirements.
Impediments:
High Introductory Tooling Cost: Making the shape can be costly, especially for complex parts.
Plan Requirements: Certain plan highlights can convolute the form plan and increment creation costs.
Key Contrasts Between Pass on Projecting and Plastic Shape Assembling
1. Materials
The essential contrast between bite the dust projecting and plastic shape fabricating lies in the materials utilized. Bite the dust projecting includes metals like aluminum and zinc, making it appropriate for parts that require strength and solidness. Plastic trim, then again, utilizes different plastics, which are more qualified for lightweight and adaptable parts.
2. Shape Plan
Bite the dust projecting molds should endure high temperatures and tensions, expecting them to be produced using solidified steel. Plastic molds, while as yet requiring accuracy, are by and large less perplexing and can be produced using steel or aluminum, contingent upon the application.
3. Creation Speed
Bite the dust projecting regularly considers quicker creation cycles because of the speedy cooling and cementing of metal. Plastic trim might demand greater investment, particularly for perplexing plans that require longer cooling periods.
4. Accuracy
Plastic Mold offers higher accuracy and more tight resistances, which is essential for parts where layered precision is fundamental. While plastic embellishment can likewise accomplish high accuracy, it may not be pretty much as predictable as kick the bucket projecting, particularly for more modest or more complicated parts.
5. Cost Contemplations
Pass on projecting as a rule includes higher beginning expenses because of the intricacy of the molds and the materials utilized. Be that as it may, it becomes financially savvy for huge creation runs. Plastic trim likewise has high forthright expenses, however the lower material expenses of plastics can go with it a more efficient decision for specific applications.
Applications in Industry
1. Pass on Projecting Applications
Pass on projecting is common in ventures where strength and solidness are fundamental. Normal applications incorporate auto motor parts, aviation parts, and electronic lodgings.
2. Plastic Embellishment Applications
Plastic embellishment is generally utilized in businesses where lightweight, adaptable parts are required. Applications incorporate purchaser gadgets, clinical gadgets, car insides, and bundling.
End
Die Casting Mold mold and plastic shape fabricating are two particular cycles, each with its own arrangement of benefits and restrictions. Kick the bucket projecting is great for delivering metal parts with high accuracy and strength, while plastic Mold embellishment is more appropriate for making adaptable, lightweight parts. Understanding the distinctions between these strategies is essential for choosing the right cycle for a given application, guaranteeing ideal outcomes concerning cost, proficiency, and quality.